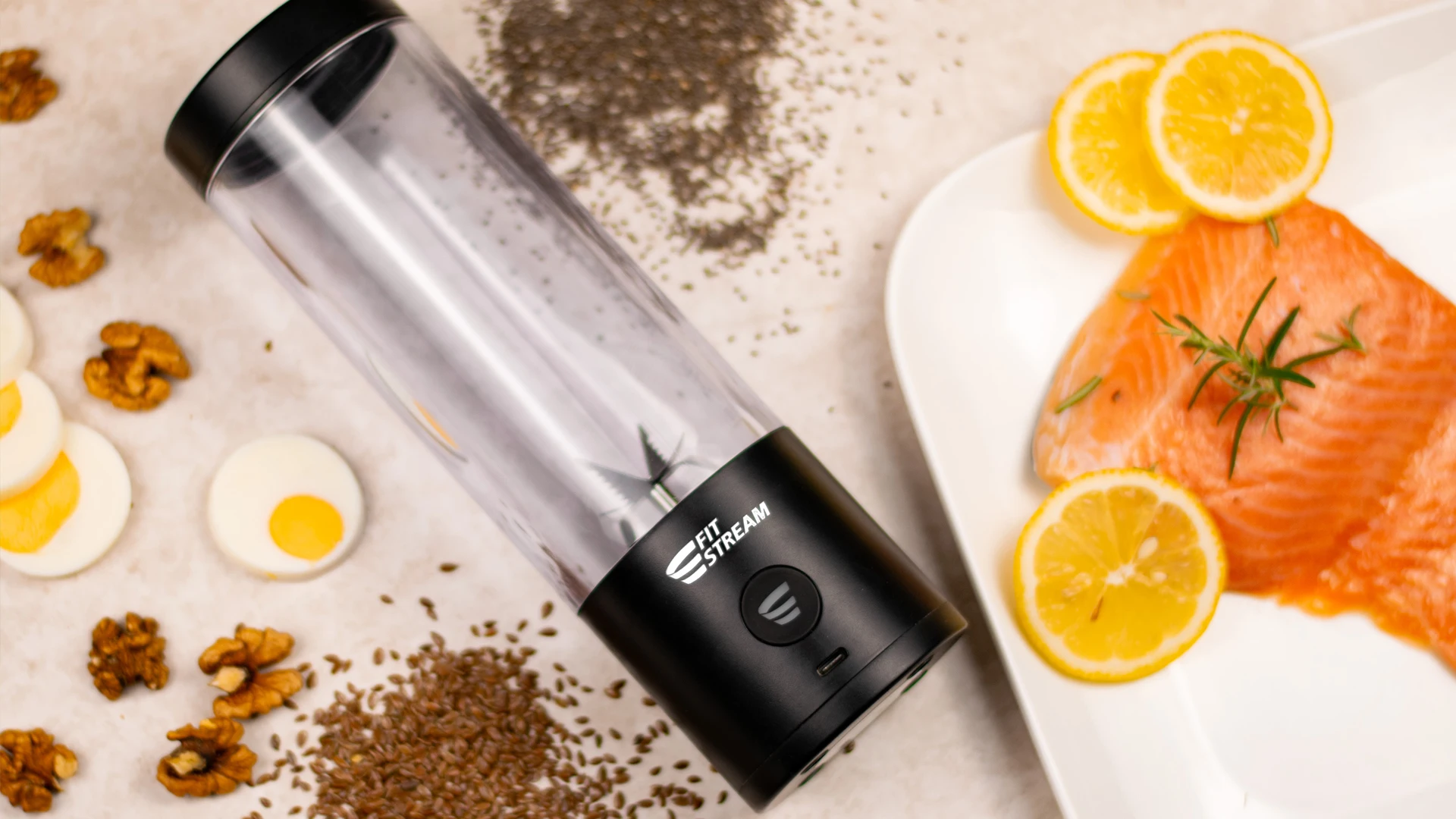
Mankind has a long history of eating fish as part of its diet. Fish and other aquatic organisms have been an important source of food for human populations throughout history, dating back to our early ancestors. Archaeological evidence, such as fish bones and tools used for fishing, suggest that early humans relied on fish as a source of food. Fish consumption likely played a key role in human evolution and the development of our species. Fish is a valuable food source that offers a number of health benefits. Including fish in our diet adds variety and diversity to our nutritional intake. Different species of fish offer a range of tastes, textures and nutritional profiles, contributing to a balanced diet.
What kind of fish do we have on our plates most often?
Europe has a diverse range of fish species that are consumed in different countries and regions. The availability and popularity of specific fish can vary, but here are some of the common fish species we eat most often:
Salmon is widely consumed in Europe and is known for its rich taste and high omega-3 fatty acid content. It is considered a fatty fish and is available in the wild in both caught and farmed alternatives. Cod is another fish often used in dishes. Herring is a small fatty fish that is often smoked, pickled or canned. It is a common ingredient in Nordic and Baltic cuisine. Mackerel is a fatty fish that is eaten grilled, smoked or canned. It is known for its distinctive taste and is rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Sardines are small fatty fish that are often canned or eaten fresh. They are packed with nutrients and omega-3 fatty acids. Trout is a freshwater fish that is widely consumed in Europe. It has a delicate flavour and is available in a variety of forms, including rainbow trout and brook trout.
Which fish are the best nutritionally?
When considering the most nutritionally appropriate fish to eat, it is important to consider its omega-3 fatty acid content, overall nutritional profile and potential environmental burden. Oily fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines and trout are particularly beneficial due to their high omega-3 fatty acid content. These fatty acids have been associated with many health benefits, including heart health, brain function and reduced inflammation.
However, it is also crucial to consider sustainability and environmental factors when selecting fish. Overfishing and destructive fishing practices can damage marine ecosystems. It is recommended to select fish species that are sustainable and have lower levels of mercury and contaminants. We can limit fish consumption to 1-3 times per week and prefer ideal fish. Some fish, especially larger predatory fish, may contain higher levels of mercury and other environmental contaminants.
What are the health benefits of eating fish?
Fish is rich in nutrients, providing us with high quality protein, vitamins and minerals. They are an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, including eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which are associated with a variety of health benefits. These omega-3 fatty acids play a key role in brain function, heart health, reducing inflammation and promoting overall well-being. Fish, especially oily fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines and trout, are rich in these beneficial omega-3 fatty acids.
Regular fish consumption is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish can help lower blood pressure, reduce triacylglycerol levels, improve blood vessel function. Omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, are important for brain health and development. They are essential for brain structure, cognitive function and may play a role in reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases (e.g. Alzheimer's disease). The omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA are beneficial for eye health. They are associated with a reduced risk of age-related macular degeneration, which is the leading cause of vision loss in older adults.
When including fish in your diet, try to eat a variety of fish, including fatty and lean fish, and be mindful of portion sizes. The American Heart Association recommends at least two servings of fatty fish per week to get the beneficial omega-3 fatty acids.
On our fitstream.eu website you will also find great nutritional supplements such as Premium Bio Matcha or collagens, which will also help your body to be in great shape.